Abstract
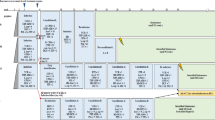
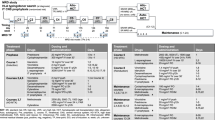
Here we report the long-term results of the DCLSG protocols ALL-6 and -7 with special emphasis on the incidence of CNS relapse after treatment without cranial irradiation. In DCLSG protocol ALL-6 (1984–1988), designed for patients with ALL non-high risk (ALL-NHR) (WBC <50 × 109/l, no mediastinal mass, no B cell phenotype and no CNS involvement at diagnosis, comprising 71% of all ALL patients), CNS prophylaxis consisted of a combination of three methods of chemotherapeutic CNS prophylaxis (the use of dexamethasone during induction and maintenance therapy, i.v. medium dose methotrexate and prolonged administration of intrathecal triple therapy). Total duration of treatment: 116 weeks. 190 patients were enrolled in the study. At 10 years, the EFS rate for all patients is 81.5 ± 2.8%, the survival rate 84.8 ± 2.7%, and the cumulative incidence of isolated CNS relapse 1.1 ± 0.8%. The 10-year survival rate for the 139/190 (73.1%) patients with standard risk non-T lineage ALL according to the NCI risk criteria is 80.5 ± 3.4%. DCLSG protocol-7 was identical to the intensive ALL-BFM-86 protocol, but cranial irradiation was restricted to patients with initial CNS involvement. Patients were stratified into three risk groups (SRG, RG and EG). Treatment duration was 18 months. 218 patients were enrolled in the study. At 10 years, the EFS rate for all patients is 63.4 ± 3.3%, the survival rate 76.4 ± 3.0%, the 5-year cumulative incidence of isolated CNS relapse 5.7 ± 1.8%. The EFS rate at 10 years of the 127/218 (58.3%) patients with standard risk non-T-lineage ALL according to the NCI risk criteria was 67.9 ± 4.3%, which is not significantly different from the results achieved in this category of patients with the moderately intensive treatment according to protocol ALL-6 (logrank P = 0.17). These DCLSG studies indicate that omission of cranial irradiation does not jeopardize the overall good results.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riehm H, Feickert HJ, Schrappe M, Henze G, Schellong G . Therapy results in five ALL-BFM studies since 1970. Complications of risk factors for prognosis Hamatol Bluttransfus 1987 30: 139–146
Langermann HJ, Henze G, Wulf M, Riehm H . Abschätzung der Tumorzellmasse bei der akuten lymphoblastischen Leukämie im Kindersalter: Prognostische Bedeutung und praktische Anwendung Klin Pädiat 1982 194: 209–213
Masera G, Gadner H, Kamps WA, Otten J, Philippe N, Schuler D, Riehm H . The treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Int J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol 1998 5: 141–144
Van der Does-van den Berg A, Bartram CR, Basso G, Benoit A, Haas OA, Harbott J, Kamps WA, Köller U, Lampert F, Ludwig W-D, Niemeyer CM, van Wering ER . Minimal requirements for the diagnosis, classification and evaluation of the treatment of childhood ALL in the ‘BFM Family’ Cooperative Group Med Pediatr Oncol 1992 20: 497–505
Reiter A, Schrappe M, Ludwig W, Hiddemann W, Sauter S, Henze G, Zimmermann M, Odenwald E, Ritter J, Gadner H, Riehm H . Chemotherapy in 998 unselected childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients Blood 1994 84: 3122–3133
Veerman AJP, Hählen K, Kamps WA, Van Leeuwen EF, De Vaan GAM, Solbu G, Suciu S, Van Wering ER, Van der Does-van den Berg A . High cure rate with a moderately intensive treatment regimen in non-high-risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of protocol ALL VI from the Dutch Childhood Leukemia Study Group J Clin Oncol 1996 14: 911–918
Kamps WA, Bökkerink JPM, Hählen K, Riehm H, Gadner H, Schrappe M, Slater R, Van den Berg-de Ruiter E, Smets LA, De Vaan GAM, Weening RS, Van Weerden JF, Van Wering ER, Van der Does-van den Berg A . Intensive treatment of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia according to ALL-BFM 86 without cranial radiotherapy: results of DCLSG Protocol ALL-7 (1988–1991) Blood 1999 94: 1226–1236
Smith M, Arthur D, Camitta B, Carroll AJ, Crist W, Gaynon P, Gelber R, Heerema N, Korn EL, Link M, Murphy S, Pui-C-H, Pullen J, Reaman G, Sallan SE, Sather H, Shuster J, Simon R, Trigg M, Tubergen D, Uckun F, Ungerleider R . Uniform approach to risk classification and treatment assignment for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia J Clin Oncol 1996 14: 18–24
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick HR, Sultan C . Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias Br J Haematol 1976 33: 451–459
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick HR, Sultan C, the French–American–British (FAB) Cooperative Group . The morphological classification of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: concordance among observers and clinical correlations Br J Haematol 1981 47: 553–561
Veerman AJP, Huismans DR, Van Zantwijk CH . Storage of cerebrospinal fluid samples at room temperature Acta Cytol 1985 29: 188–189
Van Wering ER, Veerman AJP, Van der Linden-Schrever BEM . Diagnosis of meningeal involvement in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: cytomorphology and TdT Eur J Haematol 1988 40: 250–255
Slater RM, Smeets DFCM, Hagemeijer A, De Jong B, Beverstock CG, Geraedts JPM, Van der Does-van den Berg A, Van Wering ER, Veerman AJP . Update of the cytogenetic study of childhood non-high-risk acute lymphocytic leukemia at diagnosis in protocol VI of the Dutch Childhood Leukemia Study Group Hamatol Bluttransfus 1990 33: 169–173
Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL . The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data John Wiley: New York 1980 pp 163–188
Sluis van der IM, Heuvel van den MM, Hählen K, Krenning EP, Muinck Keizer-Schrama de SMPF . Bone mineral density, body composition, and height in long-term survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood Med Pediatr Oncol 1999 33: 247 (Abstr.)
Conter V, Schrappe M, Aricò M, Reiter A, Rizzari C, Dördelmann M, Valsecchi MG, Zimmermann M, Ludwig W-D, Basso G, Masera G, Riehm H for the Associazone Italiana Ematologia Oncologia Pedriatrica and the Berlin–Frankfurt–Munster Groups . Role of cranial radiotherapy for childhood T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with high WBC count and good response to prednisone J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 2786–2791
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamps, W., Veerman, A., van Wering, E. et al. Long-term follow-up of Dutch Childhood Leukemia Study Group (DCLSG) protocols for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, 1984–1991. Leukemia 14, 2240–2246 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401964
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401964
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Long-term results of Dutch Childhood Oncology Group studies for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from 1984 to 2004
Leukemia (2010)
-
Monitoring treatment response of childhood precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the AIEOP-BFM-ALL 2000 protocol with multiparameter flow cytometry: predictive impact of early blast reduction on the remission status after induction
Leukemia (2009)
-
Early postinduction intensification therapy is essential in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Nature Clinical Practice Oncology (2008)
-
Long-term results of two consecutive trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia performed by the Spanish Cooperative Group for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Group (SHOP) from 1989 to 1998
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2008)
-
Minimal residual disease-directed risk stratification using real-time quantitative PCR analysis of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in the international multicenter trial AIEOP-BFM ALL 2000 for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Leukemia (2008)