Abstract
Purpose
Evidence suggests that while the high prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in children with Down syndrome (DS) likely contributes to sleep fragmentation, their poor sleep is only partly attributable to the presence of OSA. We hypothesized that a sleep phenotype exists for DS, which would be independent of OSA and evident across childhood.
Methods
This is a retrospective study of sleep architecture in children with DS together with matched controls. All subjects underwent baseline polysomnography between January 1985 and January 2013. Case-control pairs were compared according to age group.
Results
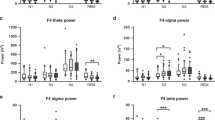
Sleep characteristics were compared in 130 DS subjects aged 0–17.8 years (median 5.8 years) and 130 matched controls. Body mass index z-scores were similar between cases and controls. Compared to controls, children with DS had a lower sleep efficiency and higher percentage of slow-wave sleep at 2–6.9, 7–11.9, and 12–17.9 years (p <0.05 for all) as well as reduced rapid-eye movement (REM) sleep percentage, significant at 7–11.9 years (p <0.05). Children with DS exhibited increased N1 sleep at 2–6.9 years but decreased N1 sleep at 12–17.9 years compared to controls (p <0.05 for both).
Conclusions
Children with DS exhibit altered sleep architecture when compared to non-DS children of similar age and OSA severity. Notably, reduced REM sleep and increased slow-wave sleep was seen independent of OSA in children with DS over 2 years. Amounts of both REM and non-REM sleep may have important implications for learning, memory, and behavior, all the more significant in this population with baseline neurocognitive impairment.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DS:
-
Down syndrome
- OSA:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea
- PSG:
-
Polysomnography
- REM:
-
Rapid eye movement
- NREM:
-
Non-rapid eye movement
- TST:
-
Total sleep time
- AHI:
-
Apnea/hypopnea index
- SFI:
-
Sleep fragmentation index
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
References
Irving C, Basu A, Richmond S, Burn J, Wren C (2008) Twenty-year trends in prevalence and survival of Down syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 16:1336–1340
Sherman SL, Allen EG, Bean LH, Freeman SB (2007) Epidemiology of Down syndrome. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 13:221–227
Sommer C, Henrique-Silva F (2008) Trisomy 21 and Down syndrome: a short review. Braz J Biol 68:447–452
Bittles AH, Bower C, Hussain R, Glasson EJ (2007) The four ages of Down syndrome. Eur J Public Health 17:221–225
Bittles AH, Glasson EJ (2004) Clinical, social, and ethical implications of changing life expectancy in Down syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol 46:282–286
Dyken ME, Lin-Dyken DC, Poulton S, Zimmerman MB, Sedars E (2003) Prospective polysomnographic analysis of obstructive sleep apnea in Down syndrome. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 157:655–660
de Miguel-Diez J, Villa-Asensi JR, Alvarez-Sala JL (2003) Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in children with Down syndrome: polygraphic findings in 108 children. Sleep 26:1006–1009
Shott SR, Amin R, Chini B, Heubi C, Hotze S, Akers R (2006) Obstructive sleep apnea: should all children with Down syndrome be tested? Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:432–436
Ng DK, Hui HN, Chan CH, Kwok KL, Chow PY, Cheung JM, Leung SY (2006) Obstructive sleep apnoea in children with Down syndrome. Singap Med J 47:774–779
Fitzgerald DA, Paul A, Richmond C (2007) Severity of obstructive apnoea in children with Down syndrome who snore. Arch Dis Child 92:423–425
Marcus CL, Keens TG, Bautista DB, von Pechmann WS, Ward SL (1991) Obstructive sleep apnea in children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics 88:132–139
Marcus CL, Brooks LJ, Draper KA, Gozal D, Halbower AC, Jones J, Schechter MS, Ward SD, Sheldon SH, Shiffman RN, Lehmann C, Spruyt K, American Academy of Pediatrics (2012) Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics 130:e714–e755
Allanson JE, O’Hara P, Farkas LG, Nair RC (1993) Anthropometric craniofacial pattern profiles in Down syndrome. Am J Med Genet 47:748–752
Silverman M (1988) Airway obstruction and sleep disruption in Down’s syndrome. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296:1618–1619
Halbower AC, Degaonkar M, Barker PB, Earley CJ, Marcus CL, Smith PL, Prahme MC, Mahone EM (2006) Childhood obstructive sleep apnea associates with neuropsychological deficits and neuronal brain injury. PLoS Med 3:e301
Andreou G, Galanopoulou C, Gourgoulianis K, Karapetsas A, Molyvdas P (2002) Cognitive status in Down syndrome individuals with sleep disordered breathing deficits (SDB). Brain Cogn 50:145–149
Stores G (1999) Children’s sleep disorders: modern approaches, developmental effects, and children at special risk. Dev Med Child Neurol 41:568–573
Levanon A, Tarasiuk A, Tal A (1999) Sleep characteristics in children with Down syndrome. J Pediatr 134:755–760
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson A, Quan S (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications, 1st edn. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Westchester
American Thoracic Society (1996) Standards and indications for cardiopulmonary sleep studies in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:866–878
Ogden CL, Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Mei Z, Guo S, Wei R, Grummer-Strawn LM, Curtin LR, Roche AF, Johnson CL (2002) Centers for disease control and prevention 2000 growth charts for the United States: improvements to the 1977 National Center for Health Statistics version. Pediatrics 109:45–60
Dijk DJ (2009) Regulation and functional correlates of slow wave sleep. J Clin Sleep Med 5:S6–S15
Trois MS, Capone GT, Lutz JA, Melendres MC, Schwartz AR, Collop NA, Marcus CL (2009) Obstructive sleep apnea in adults with Down syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med 5:317–323
Wu RH, Thorpy MJ (1988) Effect of growth hormone treatment on sleep EEGs in growth hormone-deficient children. Sleep 11:425–429
Kahn A, Dan B, Groswasser J, Franco P, Sottiaux M (1996) Normal sleep architecture in infants and children. J Clin Neurophysiol 13:184–197
Miano S, Bruni O, Elia M, Scifo L, Smerieri A, Trovato A, Verrillo E, Terzano MG, Ferri R (2008) Sleep phenotypes of intellectual disability: a polysomnographic evaluation in subjects with Down syndrome and Fragile-X syndrome. Clin Neurophysiol 119:1242–1247
Castaldo V (1969) Down’s syndrome: a study of sleep patterns related to level of mental retardation. Am J Ment Defic 74:187–190
Colas D, London J, Gharib A, Cespuglio R, Sarda N (2004) Sleep-wake architecture in mouse models for Down syndrome. Neurobiol Dis 16:291–299
Jus K, Kiljan A, Kubacki A, Losieczko T, Wilczak H, Jus A (1969) Experimental studies on memory during slow sleep stages and REM stages. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 27:668
Fishbein W (1971) Disruptive effects of rapid eye movement sleep deprivation on long-term memory. Physiol Behav 6:279–282
Hamaguchi H, Hashimoto T, Mori K, Tayama M (1989) Sleep in the Down syndrome. Brain Dev 11:399–406
Shete MM, Stocks RM, Sebelik ME, Schoumacher RA (2010) Effects of adeno-tonsillectomy on polysomnography patterns in Down syndrome children with obstructive sleep apnea: a comparative study with children without Down syndrome. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74:241–244
Robinson AM, Richdale AL (2004) Sleep problems in children with an intellectual disability: parental perceptions of sleep problems, and views of treatment effectiveness. Child Care Health Dev 30:139–150
Rihtman T, Tekuzener E, Parush S, Tenenbaum A, Bachrach SJ, Ornoy A (2010) Are the cognitive functions of children with Down syndrome related to their participation? Dev Med Child Neurol 52:72–78
Churchill SS, Kieckhefer GM, Landis CA, Ward TM (2012) Sleep measurement and monitoring in children with Down syndrome: a review of the literature, 1960–2010. Sleep Med Rev 16:477–488
Acknowledgments
Dr. O’Brien was partially supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K23 HL095739, R21 HL089918, and R21 HL087819).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nisbet, L.C., Phillips, N.N., Hoban, T.F. et al. Characterization of a sleep architectural phenotype in children with Down syndrome. Sleep Breath 19, 1065–1071 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1094-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-014-1094-6