Abstract
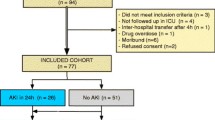
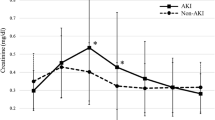
We conducted a prospective study in pediatric patients presenting to an emergency center (EC) to (1) test the ability of urinary acute kidney injury (AKI) biomarkers to predict AKI presence and severity and (2) determine if these biomarkers offer similar precision in patients with versus without a known baseline SCr. The accuracy of five putative urinary biomarkers to detect AKI presence and severity was evaluated in 252 children presenting to our EC. AKI was defined by the modified pediatric RIFLE (pRIFLE) system. Eighteen children had AKI by pRIFLE, yet 33–50% of these AKI cases may have been missed since the EC SCr was <1 mg/dl. Urinary NGAL, Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1) and beta-2 microglobulin (β2M) all demonstrated good to very good accuracy (AUC > 0.70 to 0.80) to predict patients with pRIFLE-Injury (>50% decrease in eCCl) versus patients with pRIFLE-Risk (25–50% decrease in eCCl) or without AKI. Our data suggest urinary biomarkers may serve well to detect AKI accurately in the pediatric EC setting, even in cases where SCr levels are normal. Further study is required to determine if these biomarkers obtained in the EC can predict AKI development or progression in hospitalized patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waikar SS, Bonventre JV (2008) Biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract 109:c192–c197
Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW (2005) Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3365–3370
Price JF, Mott AR, Dickerson HA, Jefferies JL, Nelson DP, Chang AC, O'Brian Smith E, Towbin JA, Dreyer WJ, Denfield SW, Goldstein SL (2008) Worsening renal function in children hospitalized with decompensated heart failure: evidence for a pediatric cardiorenal syndrome? Pediatr Crit Care Med 9:279–284
Parikh CR, Jani A, Melnikov VY, Faubel S, Edelstein CL (2004) Urinary interleukin-18 is a marker of human acute tubular necrosis. Am J Kidney Dis 43:405–414
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365:1231–1238
Parikh CR, Jani A, Mishra J, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P (2006) Urine NGAL and IL-18 are predictive biomarkers for delayed graft function following kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 6:1639–1645
Trachtman H, Christen E, Cnaan A, Patrick J, Mai V, Mishra J, Jain A, Bullington N, Devarajan P (2006) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalcin in D+HUS: a novel marker of renal injury. Pediatr Nephrol 21:989–994
Brunner HI, Mueller M, Rutherford C, Passo MH, Witte D, Grom A, Mishra J, Devarajan P (2006) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of nephritis in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54:2577–2584
Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Ma Q, Devarajan P, Parikh CR, Goldstein SL (2007) Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care 11:R84
Washburn KK, Zappitelli M, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Yalavarthy R, Parikh CR, Edelstein CL, Goldstein SL (2008) Urinary interleukin-18 is an acute kidney injury biomarker in critically ill children. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:566–572
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A (2009) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 54:1012–1024
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P (2004) Acute renal failure: definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 8:R204–R212
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A (2007) Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11:R31
Nickolas TL, O'Rourke MJ, Yang J, Sise ME, Canetta PA, Barasch N, Buchen C, Khan F, Mori K, Giglio J, Devarajan P, Barasch J (2008) Sensitivity and specificity of a single emergency department measurement of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for diagnosing acute kidney injury. Ann Intern Med 148:810–819
Shapiro NI, Trzeciak S, Hollander JE, Birkhahn R, Otero R, Osborn TM, Moretti E, Nguyen HB, Gunnerson K, Milzman D, Gaieski DF, Goyal M, Cairns CB, Kupfer K, Lee SW, Rivers EP (2010) The diagnostic accuracy of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the prediction of acute kidney injury in emergency department patients with suspected sepsis. Ann Emerg Med 56:52–59.e1
Etzioni R, Kooperberg C, Pepe M, Smith R, Gann PH (2003) Combining biomarkers to detect disease with application to prostate cancer. Biostatistics 4:523–538
Schwartz GJ, Brion LP, Spitzer A (1987) The use of plasma creatinine concentration for estimating glomerular filtration rate in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am 34:571–590
Plotz FB, Bouma AB, van Wijk JA, Kneyber MC, Bokenkamp A (2008) Pediatric acute kidney injury in the ICU: an independent evaluation of pRIFLE criteria. Intensive Care Med 34:1713–1717
Palmieri T, Lavrentieva A, Greenhalgh D (2009) An assessment of acute kidney injury with modified RIFLE criteria in pediatric patients with severe burns. Intensive Care Med 35:2125–2129
Zappitelli M, Parikh CR, Akcan-Arikan A, Washburn KK, Moffett BS, Goldstein SL (2008) Ascertainment and epidemiology of acute kidney injury varies with definition interpretation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:948–954
Ozcakar ZB, Yalcinkaya F, Altas B, Ergun H, Kendirli T, Ates C, Elhan AH, Ekim M (2009) Application of the new classification criteria of the Acute Kidney Injury Network: a pilot study in a pediatric population. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1379–1384
Hoste EA, Clermont G, Kersten A, Venkataraman R, Angus DC, De Bacquer D, Kellum JA (2006) RIFLE criteria for acute kidney injury are associated with hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a cohort analysis. Crit Care 10:R73
Kellum JA, Angus DC (2002) Patients are dying of acute renal failure. Crit Care Med 30:2156–2157
Williams DM, Sreedhar SS, Mickell JJ, Chan JC (2002) Acute kidney failure: a pediatric experience over 20 years. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 156:893–900
Vachvanichsanong P, Dissaneewate P, Lim A, McNeil E (2006) Childhood acute renal failure: 22-year experience in a university hospital in southern Thailand. Pediatrics 118:e786–e791
Hui-Stickle S, Brewer ED, Goldstein SL (2005) Pediatric ARF epidemiology at a tertiary care center from 1999 to 2001. Am J Kidney Dis 45:96–101
Askenazi DJ, Feig DI, Graham NM, Hui-Stickle S, Goldstein SL (2006) 3–5 year longitudinal follow-up of pediatric patients after acute renal failure. Kidney Int 69:184–189
Goldstein SL, Currier H, Graf C, Cosio CC, Brewer ED, Sachdeva R (2001) Outcome in children receiving continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Pediatrics 107:1309–1312
Goldstein SL, Somers MJ, Baum MA, Symons JM, Brophy PD, Blowey D, Bunchman TE, Baker C, Mottes T, McAfee N, Barnett J, Morrison G, Rogers K, Fortenberry JD (2005) Pediatric patients with multi-organ dysfunction syndrome receiving continuous renal replacement therapy. Kidney Int 67:653–658
Gillespie RS, Seidel K, Symons JM (2004) Effect of fluid overload and dose of replacement fluid on survival in hemofiltration. Pediatr Nephrol 19:1394–1399
Foland JA, Fortenberry JD, Warshaw BL, Pettignano R, Merritt RK, Heard ML, Rogers K, Reid C, Tanner AJ, Easley KA (2004) Fluid overload before continuous hemofiltration and survival in critically ill children: a retrospective analysis. Crit Care Med 32:1771–1776
Hayes LW, Oster RA, Tofil NM, Tolwani AJ (2009) Outcomes of critically ill children requiring continuous renal replacement therapy. J Crit Care 24:394–400
Bennett M, Dent CL, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Grenier F, Workman R, Syed H, Ali S, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2008) Urine NGAL predicts severity of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: a prospective study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:665–673
Dent CL, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Bennett M, Mitsnefes MM, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2007) Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts acute kidney injury, morbidity and mortality after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective uncontrolled cohort study. Crit Care 11:R127
Vaidya VS, Ford GM, Waikar SS, Wang Y, Clement MB, Ramirez V, Glaab WE, Troth SP, Sistare FD, Prozialeck WC, Edwards JR, Bobadilla NA, Mefferd SC, Bonventre JV (2009) A rapid urine test for early detection of kidney injury. Kidney Int 76:108–114
Acknowledgement
Dr. Du’s Acute Care Nephrology fellowship was supported by Gambro Renal Products.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Zappitelli, M., Mian, A. et al. Urinary biomarkers to detect acute kidney injury in the pediatric emergency center. Pediatr Nephrol 26, 267–274 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-010-1673-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-010-1673-0