Abstract
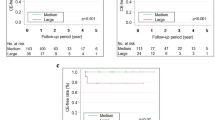
Most population-based series reporting on the coronary artery complications after Kawasaki disease (KD) originate from Japan. This study aimed to describe the complete series of KD patients from the province of Quebec in Canada, a predominantly Caucasian population. This retrospective case series was conducted by the Quebec Kawasaki Disease Registry, a multi-institutional collaboration reviewing 89.8 % of all KD cases identified by the Ministry of Health records of hospitalization for KD from the first recognized case in 1976 until 2008. This report describes the course of 38 patients (95 % Caucasians) with a diagnosis of giant coronary artery aneurysms, which represent 1.9 % of all reviewed cases and 26.2 % of those with a coronary aneurysm 5 mm or larger. The age at diagnosis was 5.52 ± 4.04 years, and the follow-up period was 9.26 ± 6.9 years. The KD diagnosis was retrospective at autopsy in two cases and via echocardiography in four cases. The overall freedom from coronary thrombi, coronary intervention, or death was respectively 63.9, 67.5, and 85.1 %. Five deaths occurred as follows: 21 days after onset of fever (2 cases), 1.8 months after onset of fever (1 case), 1 year after retrospectively presumed but previously undiagnosed KD (1 case), and 5.7 years after a KD diagnosis (1 case of sudden cardiac death). Percutaneous transluminal coronary revascularization was attempted in four cases (1 requiring cardiac transplantation), and two other cases underwent primary bypass graft surgery. Whereas this study investigated cases of KD with severe coronary sequelae in the Province of Quebec, larger collaborative studies should be conducted for further understanding of the disease in predominantly non-Asian populations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi T, Rose V, Benson LN, Newman A, Freedom RM (1992) Outcome of coronary artery aneurysms after Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 121:689–694
Akagi T, Ogawa S, Ino T, Iwasa M, Echigo S, Kishida K, Baba K, Matsushima M, Hamaoka K, Tomita H, Ishii M, Kato H (2000) Catheter interventional treatment in Kawasaki disease: a report from the Japanese Pediatric Interventional Cardiology Investigation Group. J Pediatr 137:181–186
Alloul S, Dahdah N, Miró J (2009) Thrombus in a coronary artery aneurysm shortly after warfarin withdrawal. Pediatr Cardiol 30:188–190
Burns JC, Kushner HI, Bastian JF, Shike H, Shimizu C, Matsubara T, Turner CL (2000) Kawasaki disease: a brief history. Pediatrics 106:e27
Dahdah NS, Fournier A, Jaeggi E, van Doesburg NH, Lambert R, Dionne N, Sauvé C (1999) Segmental myocardial contractility versus perfusion in Kawasaki disease with coronary arterial aneurysm. Am J Cardiol 83:48–51
Dahdah N, Ibrahim R, Cannon L (2007) First recanalization of a coronary artery chronic total obstruction in an 11-year-old child with Kawasaki disease sequelae using the CROSSER catheter. Pediatr Cardiol 28:193–389
Dallaire F, Dahdah N (2011) New equations and a critical appraisal of coronary artery z-scores in healthy children. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24:60–74
Fujiwara H, Hmashima Y (1978) Pathology of the heart in Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 61:100–107
Fujiwara T, Fujiwara H, Hamashima H (1987) Size of coronary aneurysm as a determinant factor of the prognosis in Kawasaki disease: clinicopathologic study of coronary aneurysms. Prog Clin Biol Res 250:519–520
Fulton DR, Newburger JW (2000) Long-term cardiac sequelae of Kawasaki disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2:324–329
Furuyama H, Odagawa Y, Katoh C, Iwado Y, Ito Y, Noriyasu K, Mabuchi M, Yoshinaga K, Kuge Y, Kobayashi K, Tamaki N (2003) Altered myocardial flow reserve and endothelial function late after Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 142:149–154
Hayasaka S, Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, Oki I, Tajimi M, Ojima T, Terai M, Yanagawa H (2003) Analyses of fatal cases of Kawasaki disease in Japan using vital statistical data over 27 years. J Epidemiol 13:246–250
Holman RC, Curns AT, Belay ED, Steiner CA, Schonberger LB (2003) Kawasaki syndrome hospitalizations in the United States, 1997 and 2000. Pediatrics 112:495–501
Holman RC, Christensen KY, Belay ED, Steiner CA, Effler PV, Miyamura J, Forbes S, Schonberger LB, Melish M (2010) Racial/ethnic differences in the incidence of Kawasaki syndrome among children in Hawaii. Hawaii Med J 69:194–197
Kato H, Ichinose E, Kawasaki T (1986) Myocardial infarction in Kawasaki disease: clinical analyses in 195 cases. J Pediatr 108:923–927
Kato H, Sugimura T, Akagi T, Sato N, Hashino K, Maeno Y, Kazue T, Eto G, Yamakawa R (1996) Long-term consequence of Kawasaki disease: a 10- to 21-year follow-up study of 594 patients. Circulation 94:1379–1385
Lapierre C, Bitsch A, Guérin R, Garel L, Miró J, Dahdah N (2010) Follow-up chest X-ray in patients with Kawasaki disease: the significance and clinical application of coronary artery macro-calcification. Pediatr Cardiol 31:56–61
Levy DM, Silverman ED, Massicotte MP, McCrindle BW, Yeung RS (2005) Long-term outcomes in patients with giant aneurysms secondary to Kawasaki disease. J Rheumatol 32:928–934
Manlhiot C, Brandão LR, Somji Z, Chesney AL, MacDonald C, Gurofsky RC, Sabharwal T, Chahal N, McCrindle BW (2010) Long-term anticoagulation in Kawasaki disease: initial use of low-molecular-weight heparin is a viable option for patients with severe coronary artery abnormalities. Pediatr Cardiol 31:834–842
Manlhiot C, Millar K, Golding F, McCrindle BW (2010) Improved classification of coronary artery abnormalities based only on coronary artery z-scores after Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 31:242–249
McCrindle BW, Li JS, Minich LL, Colan SD, Atz AM, Takahashi M, Vetter VL, Gersony WM, Mitchell PD, Newburger JW (2007) Pediatric Heart Network Investigators Coronary artery involvement in children with Kawasaki disease: risk factors from analysis of serial normalized measurements. Circulation 116:174–179
Nakamura Y, Aso E, Yashiro M, Uehara R, Watanabe M, Tajimi M, Oki I, Ojima T, Yanagawa H, Kawasaki T (2005) Mortality among persons with a history of Kawasaki disease in Japan: can paediatricians safely discontinue follow-up of children with a history of the disease but without cardiac sequelae? Acta Paediatr 94:429–434
Nakano H, Ueda K, Saito A, Nojima K (1985) Repeated quantitative angiograms in coronary arterial aneurysm in Kawasaki disease. Am J Cardiol 56:846–851
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, Pallasch TJ, Falace DA, Taubert KA (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation 110:2747–2771
Olivieri L, Arling B, Friberg M, Sable C (2009) Coronary artery z-score regression equations and calculators derived from a large heterogeneous population of children undergoing echocadiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 22:159–164
Pantos I, Patatoukas G, Katritsis DG, Efstathopoulos E (2009) Patient radiation doses in interventional cardiology procedures. Curr Cardiol Rev 5:1–11
Research Committee on Kawasaki disease (1984) Report of subcommittee on standardization of diagnostic criteria and reporting of coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Tokyo, Japan
Sasaguri Y, Kato H (1982) Regression of aneurysms in Kawasaki disease: a pathological study? J Pediatr 100:225–231
Suda K, Iemura M, Nishiono H, Teramachi Y, Koteda Y, Kishimoto S, Kudo Y, Itoh S, Ishii H, Ueno T, Tashiro T, Nobuyoshi M, Kato H, Matsuishi T (2011) Long-term prognosis of patients with Kawasaki disease complicated by giant coronary aneurysms: a single-institution experience. Circulation 123:1836–4218
Sugahara Y, Ishii M, Muta H, Iemura M, Matsuishi T, Kato H (2008) Warfarin therapy for giant aneurysm prevents myocardial infarction in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 29:398–401
Sugimura T, Kato H, Inoue O, Takagi J, Fukuda T, Sato N (1992) Vasodilatory response of the coronary arteries after Kawasaki disease: evaluation by intracoronary injection of isosorbide dinitrate. J Pediatr 121:684–688
Takahashi M, Mason W, Lewis AB (1987) Regression of coronary aneurysms in patients with Kawasaki syndrome. Circulation 75:387–394
Tanaka N, Naoe S, Masuda H, Ueno T (1986) Pathological study of sequelae of Kawasaki disease (MCLS), with specific reference to the heart and coronary arterial lesions. Acta Pathol Jpn 36:1513–1527
Tatara K, Kusakawa S, Itoh K, Honma S, Hashimoto K, Kazuma N, Lee K, Asai T, Murata M (1991) Collateral circulation in Kawasaki disease with coronary occlusion or severe stenosis. Am Heart J 121:797–802
Tsuda E, Kamiya T, Ono Y, Kimura K, Kurosaki K, Echigo S (2005) Incidence of stenotic lesions predicted by acute phase changes in coronary arterial diameter during Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 26:73–79
Uehara R, Nakamura Y, Yanagawa H (2005) Epidemiology of Kawasaki disease in Japan. Jpn Med Assoc J 48:183–193
Velasco-Sanchez D, Lambert R, Turpin S, Laforge S, Fournier A, Lapierre C, Dahdah N (2012) Right ventricle myocardial perfusion scintigraphy: feasibility and expected values in children. Pediatr Cardiol 33:295–301
Yamakawa R, Ishii M, Sugimura T, Akagi T, Eto G, Iemura M, Tsutsumi T, Kato H (1998) Coronary endothelial dysfunction after Kawasaki disease: evaluation by intracoronary injection of acetylcholine. J Am Coll Cardiol 31:1074–1080
Acknowledgments
This work was partially funded by Foundation En Coeur, Foundation des enfants cardiaques du Québec.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was conducted on behalf of the Quebec Kawasaki Disease Registry collaborative group.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McNeal-Davidson, A., Fournier, A., Scuccimarri, R. et al. The Fate and Observed Management of Giant Coronary Artery Aneurysms Secondary to Kawasaki Disease in the Province of Quebec: The Complete Series Since 1976. Pediatr Cardiol 34, 170–178 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-012-0409-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-012-0409-2