Abstract
Objective
To study morphine pharmacokinetics in neonates undergoing venoarterial ECMO and to quantify differences between these neonates and neonates subjected to noncardiac major surgery.
Design and setting
Observational study in a level III referral center.
Patients and methods
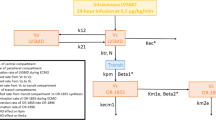
Pharmacokinetic estimates from 14 neonates undergoing ECMO were compared with findings from a previous study in 0- to 3-year-olds after noncardiac major surgery using a nonlinear mixed effect model. A one-compartment linear disposition model with zero-order input (infusion) and first-order elimination was used to describe all data.
Results
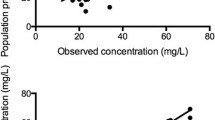
Clearance in neonates (age <7 days) at the start of ECMO (2.2 l per hour per 70 kg) was lower than that in postoperative neonates (10.5 l per hour per 70 kg) but increased rapidly (maturation half-life 30 and 70 days, respectively) and equaled that of the postoperative group after 14 days. Clearance was affected by size and age only. Exchange transfusion, when used, contributed only 1.1% (CV 46%) of total clearance. Distribution volume increased with age and was 2.5 times (CV 102%) greater in ECMO children than in postoperative children. The between-subject variability values for volume of distribution and clearance were 49.4% and 38.7%. Weight and age information explained 83% of the overall clearance variability and 60% of overall distribution volume variability.
Conclusions
Morphine clearance is reduced in infants requiring ECMO, possibly reflecting severity of illness. Clearance maturation on ECMO is rapid and normalizes within 2 weeks. Initial morphine dosing may be guided by age and weight, but clearance and distribution volume changes (and their variability) during prolonged ECMO suggests that morphine therapy should be subsequently guided by clinical monitoring.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dagan O, Klein J, Bohn D, Koren G (1994) Effects of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation on morphine pharmacokinetics in infants. Crit Care Med 22:1099–1101
Dagan O, Klein J, Gruenwald C, Bohn D, Barker G, Koren G (1993) Preliminary studies of the effects of extracorporeal membrane oxygenator on the disposition of common pediatric drugs. Ther Drug Monit 15:263–266
Geiduschek JM, Lynn AM, Bratton SL, Sanders JC, Levy FH, Haberkern CM, O’Rourke PP (1997) Morphine pharmacokinetics during continuous infusion of morphine sulfate for infants receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit Care Med 25:360–364
Buck ML (2003) Pharmacokinetic changes during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: implications for drug therapy of neonates. Clin Pharmacokinet 42:403–417
Bouwmeester NJ, Hop WC, Van Dijk M, Anand KJ, Van Den Anker JN, Tibboel D (2003) Postoperative pain in the neonate: age-related differences in morphine requirements and metabolism. Intensive Care Med 29:2009–2015
Hartley R, Quinn MW, Levene MI (1993) Morphine glucuronidation in premature neonates. Br J Clin Pharmacol 35:314–317
Hartley R, Green M, Quinn MW, Rushforth JA, Levene MI (1994) Development of morphine glucuronidation in premature neonates. Biol Neonate 66:1–9
Lynn AM, Nespeca M, Bratton SL, Strauss SG, Shen DD (1998) Clearance of morphine in postoperative infants during intravenous infusion: the influence of age and surgery. Anesth Analg 86:958–963
Lynn AM, Nespeca M, Bratton SL, Shen DD (2000) Intravenous morphine in postoperative infants: intermittent bolus dosing versus targeted continuous infusions. Pain 88:89–95
McRorie TI, Lynn AM, Nespeca M, Opheim KE, Slattery JT (1992) The maturation of morphine clearance and metabolism. Am J Dis Child 146:972–976
Lingen RA van, Simons SH, Anderson BJ, Tibboel D (2002) The effects of analgesia in the vulnerable infant during the perinatal period. Clin Perinatol 29:511–534
Bouwmeester J, Andersen B, Tibboel D, Holford NH (2004) Developmental pharmacokinetics of morphine and metabolites in neonates, infants, and children. Br J Anaesth 92:208–217
West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ (1997) A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science 276:122–126
West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ (1999) The fourth dimension of life: fractal geometry and allometric scaling of organisms. Science 284:1677–1679
Holford NHG (1996) A size standard for pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet 30:329–332
Anderson BJ, Meakin GH (2002) Scaling for size: some implications for paediatric anaesthesia dosing. Paediatr Anaesth 12:205–219
Anderson B (2004) Disentangling PK-PD in neonates. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 89:F3–F4
Bouwmeester NJ, van den Anker JN, Hop WC, Anand KJ, Tibboel D (2003) Age- and therapy-related effects on morphine requirements and plasma concentrations of morphine and its metabolites in postoperative infants. Br J Anaesth 90:642–652
Verwey-van Wissen CP, Koopman-Kimenai PM, Vree TB (1991) Direct determination of codeine, norcodeine, morphine and normorphine with their corresponding O-glucuronide conjugates by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr 570:309–320
Kimenai PM (1996) Clinical pharmacokinetics of nicomorphine. Metabolic conversion: an important aspect of drug action. Thesis, Catholic University, Nijmegen
Beal SL, Sheiner LB, Boeckmann A (1999) Nonmem user’s guide. Division of Pharmacology, University of California, San Francisco
Peters HP (1983) Physiological correlates of size. In: Beck E, Birks HJB, Conner EF (eds) The ecological implications of body size. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 48–53
Karalis V, Macheras P (2002) Drug disposition viewed in terms of the fractal volume of distribution. Pharm Res 19:696–703
Carcillo JA, Doughty L, Kofos D, Frye RF, Kaplan SS, Sasser H, Burckart GJ (2003) Cytochrome P450 mediated-drug metabolism is reduced in children with sepsis-induced multiple organ failure. Intensive Care Med 29:980–984
Fisher MB, Vandenbranden M, Findlay K, Burchell B, Thummel KE, Hall SD, Wrighton SA (2000) Tissue distribution and interindividual variation in human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity: relationship between UGT1A1 promoter genotype and variability in a liver bank. Pharmacogenetics 10:727–739
Berkenstadt H, Segal E, Mayan H, Almog S, Rotenberg M, Perel A, Ezra D (1999) The pharmacokinetics of morphine and lidocaine in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 25:110–112
Pokela M, Olkkola KT, Seppälä T, Koivisto M (1993) Age-related morphine kinetics in infants. Dev Pharmacol Ther 20:26–34
Dagan O, Klein J, Bohn D, Barker G, Koren G (1993) Morphine pharmacokinetics in children following cardiac surgery: effects of disease and inotropic support. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 7:396–398
Hunt A, Joel S, Dick G, Goldman A (1999) Population pharmacokinetics of oral morphine and its glucuronides in children receiving morphine as immediate-release liquid or sustained-release tablets for cancer pain. J Pediatr 135:47–55
Mulla H, McCormack P, Lawson G, Firmin RK, Upton DR (2003) Pharmacokinetics of midazolam in neonates undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Anesthesiology 99:275–282
Milne RW, McLean CF, Mather LE, Nation RL, Runciman WB, Rutten AJ, Somogyi AA (1997) Influence of renal failure on the disposition of morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide and morphine-6-glucuronide in sheep during intravenous infusion with morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:779–786
Osborne R, Joel S, Grebenik K, Trew D, Slevin M (1993) The pharmacokinetics of morphine and morphine glucuronides in kidney failure. Clin Pharmacol Ther 54:158–167
Dagan O, Klein J, Bohn D, Barker G, Koren G (1993) Morphine pharmacokinetics in children following cardiac surgery: effects of disease and inotropic support. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 7:396–398
Mao J, Price DD, Mayer DJ (1995) Mechanisms of hyperalgesia and morphine tolerance: a current view of their possible interactions. Pain 62:259–274
Dijk van M, Boer de JB, Koot HM, Passchier J, Tibboel D, Duivenvoorden HJ (2000) The reliability, stability and validity of the COMFORT scale as a postoperative pain instrument in 0 to 3-year-old infants. Pain 84:367–377
Peters JWB, Koot HM, Grunau RE, De Boer J, Van Druenen MJ, Tibboel D, Duivenvoorden HJ (2003) Neonatal facial coding system for assessing postoperative pain in infants: item reduction is valid and feasible. Clin J Pain 19:353–363
Ambuel B, Hamlett KW, Marx CM, Blumer JL (1992) Assessing distress in pediatric intensive care environments: the COMFORT scale. J Pediatr Psychol 17:95–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, J.W.B., Anderson, B.J., Simons, S.H.P. et al. Morphine pharmacokinetics during venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in neonates. Intensive Care Med 31, 257–263 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-004-2545-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-004-2545-5